Being a field of diverse directions and numerous purposes, the design has always brought up a lot of issues at the crossroads of professional activities and sciences. It’s time for a new set of answers covering the frequently asked questions in the domains of web, mobile, and graphic design: having given a big bunch of answers on Quora recently, we would like to share our ideas with Tubik Blog readers as well. So, today we are briefly covering the following topics:
- Is it important for a small business to have a website?
- How can UI/UX design strategically influence a company’s success?
- What motivates mobile-app start-ups to hire UX designers?
- Who buys graphic design services?
Let’s get started!

How important is it for a small business to have a website?
In short: if you can reach your customers via the Internet, it IS important to think about a website for your business.
Going deeper, we can face a lot of pathetic expressions saying the main and only reason is that everything is on the Internet now. I wouldn’t be so categorical on that. Real life still exists, and some businesses, especially small local ones, effectively operate without websites in their own vision of success. Not all businesses strive to conquer the world – and it doesn’t leave us right to tell they aren’t successful or helpful or effective or profitable. Let’s say, you live in a quiet small village and supply local citizens with home-made cheese. You have your own range of clients and you have no reasons to move further as all the cheese you may produce with your capacities is bought like hotcakes. The profits you get are enough for your vision of a peaceful and successful life. Is it a small business? Yes, sure. Does it need a website? According to the stakeholder’s goals, no, it doesn’t.
However, the Internet really revolutionized the way of running businesses. With devices cheaper, more accessible, and easy-to-use, more and more people turn to buying, selling, marketing, communicating, and getting information from the internet resources. So, today it’s one of the top reasons why people make a decision on starting a website: they have an offer that may be potentially interesting to other people on the Web and bring the profits to the entrepreneur.
This way to go is really reasonable, and there is a huge variety of approaches to websites for business use. It can be anything, from a simple one-page website giving the basic description of the professional and contact data to complex web platforms providing a variety of business directions or extensive portfolio. It may be a small e-commerce platform, with a full cycle of direct sales from order to payment and delivery, or it may be a corporate website whose aim is to present the services or goods as well as the ways of getting them. This can be the reason for not only fully packed websites of broad functionality but also landing pages fulfilling the same need.

Having a website, the business gets a broader perspective and becomes closer to users, who are often used to googling as the fastest way to find everything they need, from basic goods to special services. If your potential clients can be caught in this process of browsing, you definitely have to try it and a company website is a primary step. Nevertheless, it’s important to remember that the website will become another item in your budget: time, effort, and in all likelihood money will be invested in website creation and maintenance. For big and well-established businesses it may be not a pinch of a problem but for a small business, it is a concern demanding to weigh all pros and cons. So, on the stage of decision-making, it’s cool to discuss the issue with experts and other businessmen, read the case studies and reviews to know what the possible further scenarios may happen, how important they are for the business growth, and what you would better start with.

The reasons, which might get you to hesitate if you need your own website being a small business, can be the following:
- the specific nature of the business doesn’t make it possible and viable to reach your clients online
- the expenses on the website aren’t reasonable and do not open real perspectives on the business growth
- the small business has another alternative platform for its activity which is profitable for its aims (for example, you make hand-crafted toys which are successfully bought via Etsy-shop and it creates a strong online presence for the business).
Anyway, if the business strives to transfer from small to medium or big and isn’t going to spend ages for it, the website is a worthy investment.
How can UI/UX design strategically influence company success?
There are several aspects to consider, first of all depending on the type of business activity and relations. Among the cases when web and mobile UX design can significantly influence company performance, we could mention the following ones.
1. The company gets its profits via a digital product
In this case, UX/UI is definitely one of the core issues influencing the growth, progress, and success of the company. Thoughtful UX (logics, transitions, the flow of user journey and interactions) and effective UI (visual performance, typography, visual hierarchy, emotional appeal, and aesthetic satisfaction) lay the solid foundation for achieving business goals set behind the digital product and therefore profits of the company.
Why is it so? Because the UX/UI design:
- strengthens the brand image and enhances brand awareness
- enables users to solve their problems with the product demonstrating a high level of usability
- supports efficient sales funnel and educates a user about the product
- applies visual hierarchy to make navigation through the interface intuitive and in this way grows the level of conversion
- transforms the tone and voice of the product as well as a flow of interactions that are appropriate for a particular target audience.
As it was mentioned in the book Design For Business, the offer is the key. Design is an actionable and helpful tool on every stage of launching, presenting, and promoting the product, informing users about it, and selling it in a fast and easy way. Nevertheless, if the product is of poor quality, a successful design isn’t going to make it better. Think about the product and its user first, only then the design will give it the chance to beam at full.
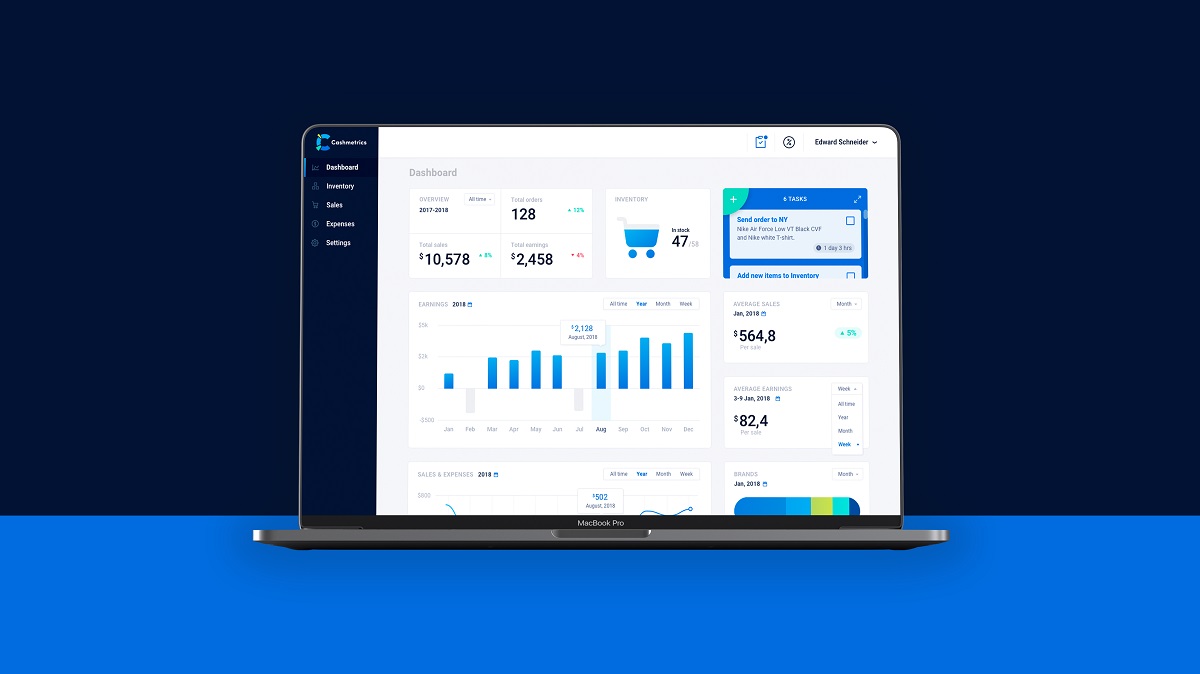
2. The company presents an e-commerce platform
Obviously, the success of ecommerce activity depends on several factors among which:
– quality of the product or service offered
– quality of the content presenting the offer to customers
– quality of design for the electronic platform — website and/or mobile application — via which the sales are going to be delivered.
So, it’s easy to see that the UI/UX design part plays a vital role. Thoroughly thought-out logic and transitions, simple and clear microinteractions, fast feedback from the system, attractive product presentation, easy payment flow, and plenty of other details and features can directly influence increasing profits for the business involved in such a popular e-commerce game. This is the field where designers and business experts can work as one team for good of everyone, first of all of the target users.
3. The company uses the digital tools and services for communication of its personnel and data analysis
Nowadays there are more and more companies that use apps or websites for productive communication inside the team: some of them apply external stuff, while others create the apps which correspond to their specific needs. In this case, UX again is a strategically important direction to invest time and money in: it enables employees to work more productively while managers analyze data in a fast and precise manner. These factors directly influence the rates of general profits and expenses of the company.
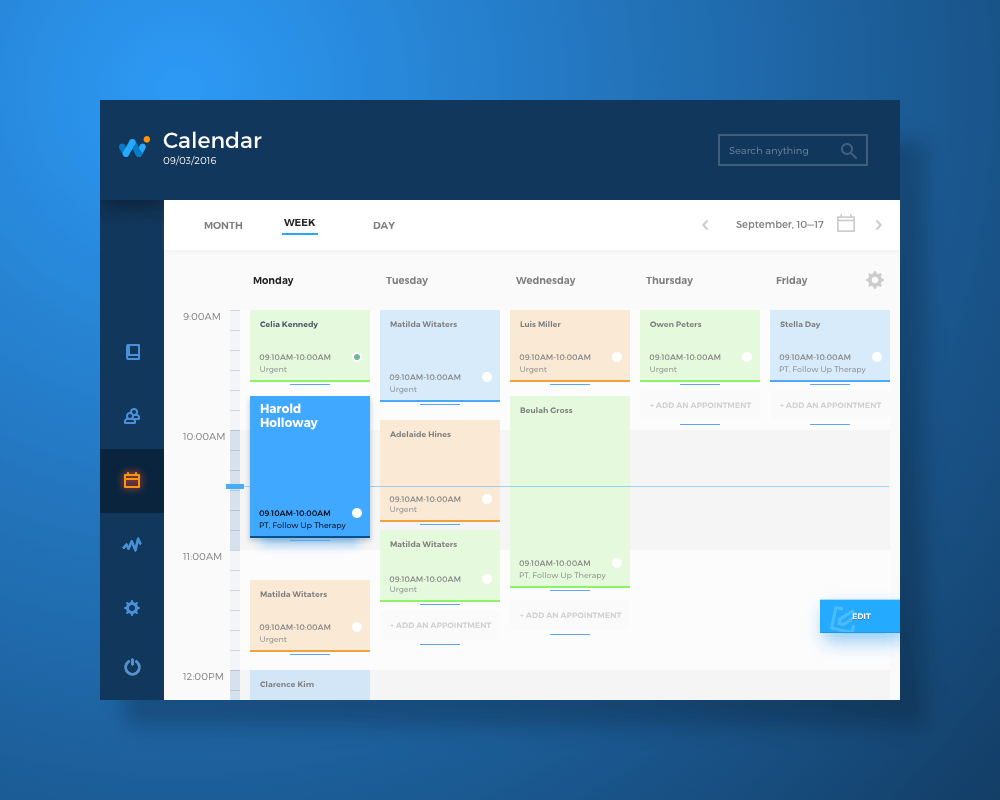
Here we’ve mentioned only three of possible directions when UI/UX contributes to general company performance, still, there are many of them. Working on different design projects here in Tubik, we’ve checked how different can business goals be but definitely, the design opens numerous ways to support them.
What motivates mobile-app start-ups to hire UX designers?
The step of hiring a UI designer for a mobile-app start-up is a very logical thing to do: the thought-out design of a digital product is a solid foundation for a nice introduction to the market. Among the factors of impact on this decision, we would mention USP and MVP which build up the bridge between business and design perspectives.
USP
A mobile app is a product that means it has its USP (Unique Selling Point). User interface design is the way to strengthen it and present it in the correct way.
If USP is defined at the pre-design stage that means that all design solutions can be made to support it. That is a good foundation for efficient branding supported by recognizable and consistent interface design which enhances better interaction and memorability. USP directly influences:
- integration of brand identity into the interface to enhance brand awareness
- building up principles of interaction and user experience in terms of efficient presentation and providing benefits of USP
- creating a problem-solving user interface that clearly reflects USP and provides the fast and easy way to get it
- creating and selecting content which will support the general design concept and show users the advantages of the product and corresponds to target audience expectations
- design of a landing page that will have the structure and content directly presenting USP to the target audience
- applying design tactics that increase the conversion of the app screens etc.
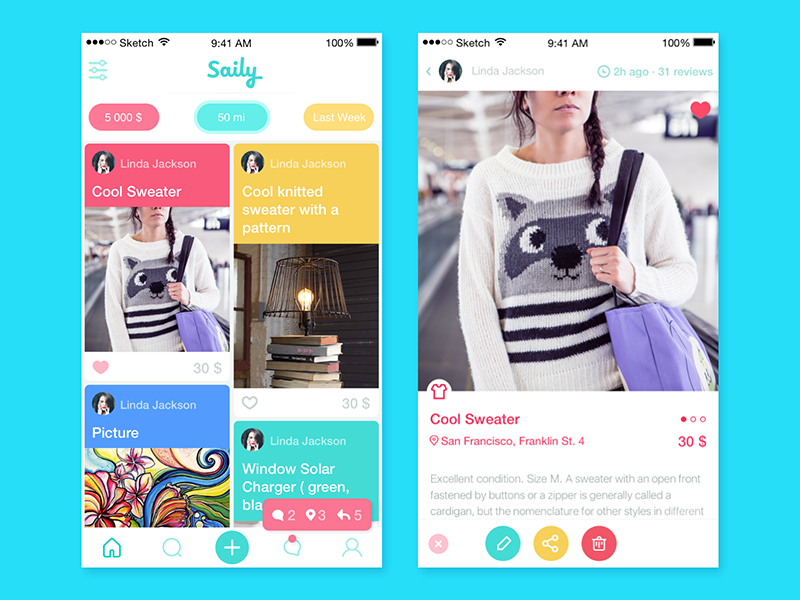
As a practical example, we can remember the story of creating UI design for Saily App, a local service of user-to-user e-commerce. The customers defined its USP from the very start: it is a local community app allowing neighbors to buy and sell their used stuff, so it provides people with the ability to sell their own things or quickly search for the needed ones sold in their location. This idea became a solid basis for all the design solutions around branding and user interface of the app, setting bright experience and friendly communication. If you are interested to read the details and see the visual design process, welcome to read case studies on logo design and UI design for the app.
MVP
Many startups follow the path of MVP (Minimum Viable Product) which is a product with a set of minimal functions and features that are logically completed and sustainable providing the most important and basic functions for the core target audience. This means that the basic version of the product, able to fulfill key operations which are solving the target audience’s problems, is created as live and starts real functioning as soon as possible. The approach is opposite to the strategy of creating a full design and comprehensive functionality for all the product features for the broader target audience and only afterward launching it on the market.
MVP approach has several benefits:
— as it starts from the simple and basic version of the product, it doesn’t take a long time to provide design and development and makes it possible to start playing on the market faster. It’s especially actual for diverse technological ideas and concepts as they are always at risk to outmode by the time all the design, development, and testing cycle is finished;
— it enables designers, testers, analysts, managers and marketing specialists to collect data of real users’ interaction with a product reveal the bugs, understand their wishes and pains deeper, and use all that information in the design and presentation of further, more complex versions of the product. Although testing should be done at the stage of development, it is impossible to predict all the potential problems of interaction with a product before real users start this interaction. MVP enables creators to do it faster and make the next versions more efficient;
— if thoughtfully made and carefully presented, MVP can play the role of bait attracting target customers and allowing its creators to see if the target audience was defined properly and analyzed deeply enough;
— next versions of MVP usually present quite massive functional additions so depending on the target it may work as the way of positive and dynamic user experience, different from slight changes in the products whose functionality was fully developed before the launch.
Therefore, in terms of design MVP is the strategy of step-by-step movement on the market, when every next step is based on the analysis of the previous one from the actual data collected from real users. That means that designers should also apply the strategy of gradual design, carefully applying only core features which are really vital for the MVP as the start of the journey. It greatly influences the number of screens and content on them, necessary transitions and notifications which users really need at this stage of using the product, level of complexity and sophistication of graphic materials and animation, etc. UX/UI designers should remember that MVP always has a definite core target audience and the solutions to interactions, experience, visual perception, etc. Knowing these core users makes the design task more particular and the result will be more customer-oriented thus efficient. The next versions of the product will provide broader functionality and in this way will broaden the circle of users, but it will work in the case when the core target audience is caught by MVP.
Successful MVP is directly connected to the USP of the product. Here USP plays an even bigger role as it enables us to make the product user-centered and in this case the chances of making it efficient and attractive to users get much higher. Presenting the product solving particular problems of a particular group of people in many cases proved itself as an effective strategy with the perspective of further growth of both functionality and audience. This strategy works especially well for various startups which start with a limited budget used wisely for the practical presentation of the vital features of the product: if MVP is thought out properly, at this first stage they already start monetization of the product, attract users and at the same time apply practical data analysis in further stages of design. It’s easy to see that the role of UI/UX design here gets even higher as MVP is actually the chance of making a good first impression. Spoiling it with bad design can have a crucially bad result for the product’s promotion as well as good design can build up a solid foundation for product growth.
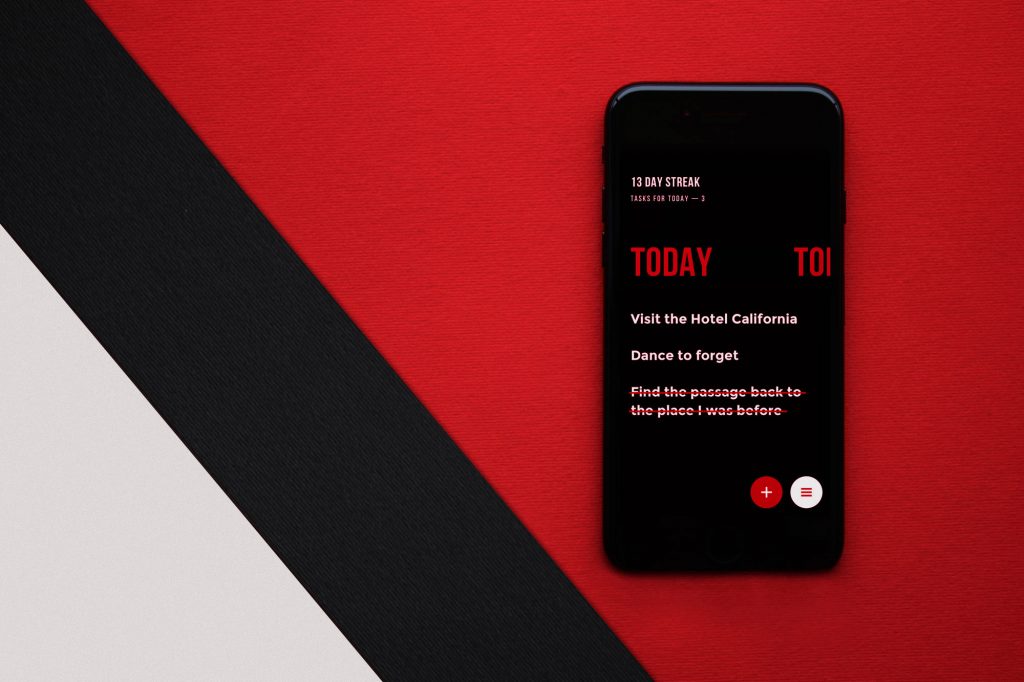
Upper App which started as an MVP
The mentioned ideas present good motives for hiring a UI designer for creating a brand new app.
Who buys graphic design services or products?
First of all, let’s quickly review what stands behind the notion of graphic design services. Basically, graphic designers do the job of communication to others by means of graphic (visual) elements such as images of different styles and complexity, types and fonts, pictograms, shapes and sizes, colors and shades, lines and curves, etc. A graphic designer makes all those elements of visual perception transfer the message, so he makes them functional. Therefore, we could say that graphic designers are artists applying their talents mostly not in pure art, but communicating and purposeful art.

Modern graphic design broadly covers all spheres of human life which deal with visual communication, from books and posters to sophisticated mobile applications or 3D animation. Let’s look into directions in which graphic designers can express their creativity for the sake of solving problems and satisfying needs, in particular, it includes:
- editorial and book design
- illustration
- identity (logo and branding) design
- icons and pictograms
- typography
- interface graphics and elements
- print advertisements
- big printed items such as posters and billboards
- signs
- infographics and mapping
- packaging, etc.

Therefore, anyone interested in getting a graphic outcome for the mentioned purposes is a potential buyer of graphic design services, in particular:
– businesses from very small to major, in need of branding, rebranding, or creating the extensive corporate identity
– people who need special original graphics to present their personal brand
– book publishers
– publishers of periodical mass-media
– advertisers
– product design teams or customers who need custom graphics for their websites and mobile applications
– diverse agencies and organizations that need posters, stickers, labels, and the like for their events, campaigns, offices, etc.
– educational institutions for creating various graphics with educational objectives (classroom posters, printables, handouts, toys and games images, etc.)
– cartoon and game creators.
Certainly, the list can be continued, still even now it’s clear that there are many variations that can become the potential customer for a graphic designer.
Today’s brief FAQ review is over, but new answers are coming very soon, stay tuned!